System maintenance strategies are key to successful industrial operations, where machinery’s performance drives productivity. Amid the tapestry of methodologies, two stand out prominently: Predictive Maintenance (PdM) and Preventive Maintenance (PM). As technology propels industries forward, the choice between these two strategies becomes paramount. In this comprehensive exploration, we dissect the nuances of Predictive Maintenance and Preventive Maintenance, unraveling their differences, advantages, and challenges. By understanding how these approaches align with the technological evolution, industry 4.0 trends, and real-world applications, businesses can equip themselves to make informed decisions that resonate with their unique operational landscapes. Join us on this journey to discover the dynamic interplay between foresight and preparedness, innovation and tradition, all in the pursuit of maintaining industrial excellence.
What is Preventive Maintenance (PM)
Preventive maintenance, or preventative maintenance, represents a proactive maintenance strategy that significantly contributes to optimal asset management. This methodology involves systematically and regularly conducting maintenance on physical assets. The primary objective of preventive maintenance is to shorten the likelihood of equipment failures and reduce machine downtime. Such unforeseen disruptions can take a heavy toll on maintenance teams and facility managers in terms of both financial costs and operational efficiency.
To execute effective preventative maintenance, meticulous planning, and scheduling are essential. This planning hinges on real-time data analytics, often harnessed through advanced software like a Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS). This software-driven approach empowers organizations to make informed decisions, optimizing maintenance schedules for maximal efficiency.
Preventive maintenance tasks are strategically performed while the equipment is still operational. This proactive measure aims to forestall unexpected breakdowns that can disrupt operations and lead to costly machine downtime. A well-structured preventive maintenance strategy positions organizations between reactive maintenance, where repairs are carried out after failure, and predictive maintenance, which relies on data-driven forecasts.
By embracing the principles of preventative maintenance, organizations not only reduce the risk of unexpected disruptions but also extend the lifecycle of their equipment. This approach ensures that assets continue performing at their peak, fostering operational continuity and enhancing long-term productivity.

🔧 Ready to Elevate Your Operations? Let’s Implement Predictive Maintenance Together! 🔧
👉 Contact Us Now for Expert Guidance! 👈
What is Predictive Maintenance (PdM)
Predictive maintenance (PdM) is a cutting-edge technique that harnesses advanced data analysis tools and methodologies to detect anomalies within your operational processes and potential defects lurking in equipment. The objective? To address these issues before they escalate to critical failures. This proactive maintenance strategy redefines how industries approach maintenance, optimizing efficiency and reliability.
The true essence of predictive maintenance lies in its capacity to predict problems well before they manifest as significant disruptions. This revolutionary approach hinges on historical and real-time data collected from diverse corners of your operation. By analyzing this data, patterns, and abnormalities are unveiled, offering insights into impending challenges.
Three key pillars shape the predictive maintenance service landscape within your organization:
1. Real-time Monitoring of Asset Condition and Performance: Predictive maintenance thrives on constant vigilance. It monitors asset condition and performance continuously, allowing for real-time adjustments and preemptive actions. This vigilant oversight ensures that deviations from the norm are identified swiftly, minimizing risks and enhancing operational stability.
2. Analysis of Work Order Data: Work order data contains valuable maintenance history and trend information. Through careful analysis of this data, predictive maintenance can unearth hidden connections and causal relationships. This in-depth scrutiny enables more accurate predictions and informed decision-making.
3. Benchmarking MRO Inventory Usage: Maintenance, Repair, and Operations (MRO) inventory usage is a critical metric. Predictive maintenance leverages this data to optimize inventory management. Organizations balance availability and cost efficiency harmoniously by aligning inventory levels with maintenance needs.
The driving force behind the predictive maintenance revolution is technology. The synergy of the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence, and integrated systems forms the backbone of this approach. These components enable diverse assets and systems to communicate, collaborate, and share data seamlessly.
Predictive maintenance tools play pivotal roles, from sensors to industrial controls and sophisticated business systems like Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software. These tools capture information, from subtle vibrations to thermal signatures. The data collected is then intelligently processed to pinpoint areas demanding attention.
For instance, vibration analysis, oil analysis, thermal imaging, and equipment observation are key avenues through which predictive maintenance sensors operate. Each method provides invaluable insights into equipment health, enabling informed decisions that prevent unplanned machine downtime and keep operations humming smoothly.
Intricately interwoven with technological prowess, predictive maintenance is not just a strategy—it’s a transformative journey towards enhanced productivity, reduced costs, and operational excellence. As industries evolve, embracing predictive maintenance becomes imperative to stay competitive in an ever-evolving landscape.

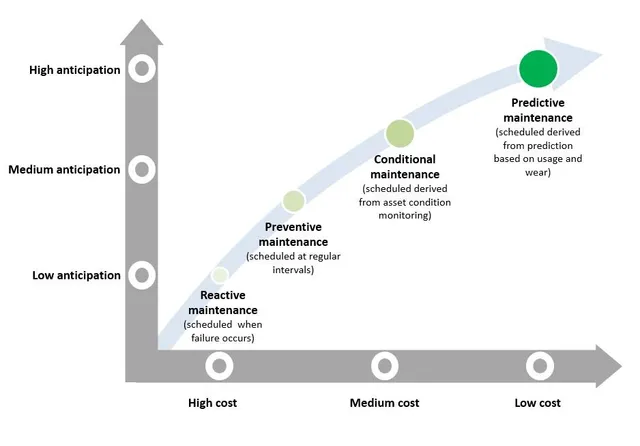
Differences and Similarities between Predictive and Preventive Maintenance
At their core, preventive and predictive maintenance converge on a common objective: enhancing asset reliability while minimizing the impact of reactive failures. The underpinning philosophy of both strategies is rooted in pre-planned maintenance activities, machine downtime reduction, and optimizing operational efficiency.
In essence, both preventive and predictive maintenance fall under the umbrella of scheduled maintenance practices. Work orders are meticulously crafted and scheduled well before the maintenance event, epitomizing proactive foresight.
Yet, within this shared realm, distinctive nuances emerge, delineating the boundaries between preventive and predictive maintenance. The crux of the distinction lies in their scheduling mechanisms and cost dynamics. Preventative maintenance follows a regular schedule, ensuring maintenance tasks occur at predetermined intervals. In contrast, predictive maintenance operates on a more dynamic schedule, hinging on the real-time conditions of the assets themselves. This dynamic scheduling imbues predictive maintenance with adaptability that prevents unnecessary maintenance and optimizes resource utilization.
While both strategies yield financial advantages, their cost dynamics vary significantly. Preventive maintenance is characterized by lower implementation costs, making it an attractive choice for organizations looking to mitigate upfront expenditures. On the other hand, predictive maintenance entails higher initial costs. The deployment of predictive maintenance necessitates substantial investments in training, technology, and resources. However, these upfront expenses often yield substantial long-term benefits by curbing labor and material costs.
Predictive maintenance’s flexibility to be performed precisely when needed further cements its cost-efficient nature. This adaptability reduces labor and material expenditures, as maintenance activities are initiated directly to asset conditions, minimizing wastage.
Although the choice between preventive and predictive maintenance involves nuanced trade-offs, organizations that successfully implement preventive maintenance often find the leap to predictive maintenance more palatable. The ability to proactively address maintenance needs and the potential for long-term cost savings make the upfront investment in predictive maintenance a strategic maneuver for organizations committed to operational excellence.
In this landscape where reliability, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness reign supreme, aligning maintenance strategies with organizational goals emerges as a crucial determinant of success. Whether embracing the steadfast predictability of preventive maintenance or delving into the adaptive realm of predictive maintenance, the ultimate goal remains unchanged: to build a resilient and optimized operational framework that propels businesses forward.
🔧 Ready to Elevate Your Operations? Let’s Implement Predictive Maintenance Together! 🔧
👉 Contact Us Now for Expert Guidance! 👈

Choosing Between Predictive and Preventive Maintenance
The decision-making process between predictive and preventive maintenance hinges on a multi-faceted evaluation encompassing various factors within an organization’s operational landscape. This pivotal choice revolves around understanding the unique equipment needs, business objectives, and the level of technological integration achievable.
Equipment Criticality and Complexity: A paramount consideration is the criticality and complexity of the equipment in question. Machinery with high operational significance or intricate components might benefit from a predictive maintenance approach. The granular insights afforded by predictive maintenance enable swift intervention before issues escalate. Conversely, less critical equipment might align better with a preventive maintenance strategy, where scheduled tasks mitigate risks.
Usage Patterns and Workload: Examining usage patterns and workload characteristics provides a lens to determine the suitable maintenance strategy. With its real-time adaptability, predictive maintenance suits equipment subjected to varying workloads. On the other hand, preventive maintenance might be ideal for machinery exposed to consistent operational demands.
Technological Readiness: Organizational readiness for data-driven approaches is pivotal. Predictive maintenance demands a robust data collection, analysis, and interpretation infrastructure. If your organization has the necessary technology and expertise, embracing predictive maintenance can offer substantial benefits. However, for businesses not yet positioned for complex data integration, preventive maintenance presents a more accessible avenue.
Maintenance Budget Considerations: Budgetary constraints play a significant role in the decision-making process. Predictive maintenance’s initial investment in technology, training, and resources might deter some organizations. With its lower upfront costs, preventive maintenance can be an attractive alternative. Organizations with the means to invest upfront find predictive maintenance’s long-term cost savings and efficiency gains compelling.
Operational Disruption Tolerance: The tolerance for operational disruptions must also be gauged. Predictive maintenance’s proactive nature minimizes unplanned machine downtime. Organizations with a low tolerance for disruptions can reap immense benefits from such a strategy. Preventive maintenance, although reducing unplanned failures, might entail scheduled downtimes that must be factored in.
The choice between predictive and preventive maintenance is a finely tuned balancing act. Organizations must assess their equipment, resources, technological readiness, and operational priorities. This decision is not binary; hybrid approaches can also be tailored to specific circumstances. An astute alignment of maintenance strategy with business goals results in an operational framework that thrives on optimized reliability, minimized costs, and enhanced efficiency.
🔧 Ready to Elevate Your Operations? Let’s Implement Predictive Maintenance Together! 🔧
👉 Contact Us Now for Expert Guidance! 👈

Challenges and Best Practices
Implementing maintenance strategies, be they predictive or preventive, is challenging. However, a proactive maintenance strategy approach to overcoming these obstacles can lead to effective and efficient maintenance operations.
Challenges:
1. Technological Integration: Integrating advanced technologies like sensors, data analytics, and predictive modeling can pose challenges. Organizations must ensure seamless compatibility with existing systems while mitigating potential disruptions during implementation.
2. Data Management: The volume and complexity of data generated in predictive maintenance can be overwhelming. Proper data management systems must be in place to handle data acquisition, storage, and analysis effectively.
3. Skill and Training: Equipping personnel with the skills to handle predictive maintenance technology is crucial. Training and upskilling initiatives are essential to utilize data-driven insights effectively.
4. Change Management: Shifting from traditional maintenance practices to data-driven approaches requires cultural change. Resistance to change can hinder successful implementation.
Best Practices:
1. Comprehensive Data Strategy: Develop a robust data strategy encompassing data collection, analysis, and interpretation. This strategy should align with the organization’s goals and provide actionable insights.
2. Cross-functional Collaboration: Foster collaboration between maintenance teams, data analysts, and equipment operators. A multidisciplinary approach ensures a holistic understanding of equipment health.
3. Continuous Monitoring: Continuous asset monitoring is crucial for predictive maintenance. Real-time data collection enables prompt intervention, reducing machine downtime.
4. Performance Benchmarking: Regularly assess the performance of your maintenance strategy. Compare the achieved results against predetermined goals to refine and optimize your approach.
5. Data Security: Prioritize data security and privacy. Implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive maintenance data from potential breaches.
6. Change Management Strategy: Implement a change management plan to ease the transition to data-driven maintenance. Communication, training, and involving stakeholders are integral components.
7. Scalability and Flexibility: Design your maintenance strategy with scalability and flexibility. As your organization grows, your maintenance approach should seamlessly adapt.
Conclusion
While challenges may arise when implementing predictive or preventive maintenance strategies, they are manageable. By adhering to best practices and maintaining a proactive mindset, organizations can navigate these challenges and unlock the full potential of their maintenance operations. Embracing technological advancements, fostering collaboration, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement are the cornerstones of success in modern maintenance practices.
Real-world Applications and Industry Insights
I am exploring real-world applications across various industries to better understand PdM and PM. For instance, the mining industry has embraced Industry 4.0 technologies to revolutionize maintenance practices. The article “The impact of technological evolution on the mining industry” provides insights into this transformation. Additionally, “The challenges of implementing Industry 4.0 and predictive maintenance and how to overcome them” sheds light on hurdles faced during adoption.
Putting it all Together: Industry 4.0 and Predictive Maintenance
The synergy between Industry 4.0 and predictive maintenance is evident in their real-world applications. Industries spanning manufacturing, energy, and more have harnessed these approaches to boost efficiency and competitiveness. Explore “Real-world applications of Industry 4.0 and predictive maintenance in different industries” for in-depth case studies.
Exploring How Predictive Maintenance Works
Curious about the inner workings of PdM? Our article “How predictive maintenance works” offers a detailed process breakdown. It provides a comprehensive overview of this innovative strategy, from data collection and analysis to actionable insights.
Conclusion
In the dynamic landscape of industrial maintenance, choosing between Predictive Maintenance and Preventive Maintenance requires a thorough understanding of your organization’s needs and capabilities. While PM adheres to scheduled tasks, PdM leverages data to predict and prevent failures. Each approach has its merits, but the key is to align your choice with your industry, equipment, and readiness for technological integration. You can ensure smoother operations, reduced downtime and enhanced profitability with the right strategy.
🔧 Ready to Elevate Your Operations? Let’s Implement Predictive Maintenance Together! 🔧
👉 Contact Us Now for Expert Guidance! 👈